What it is?
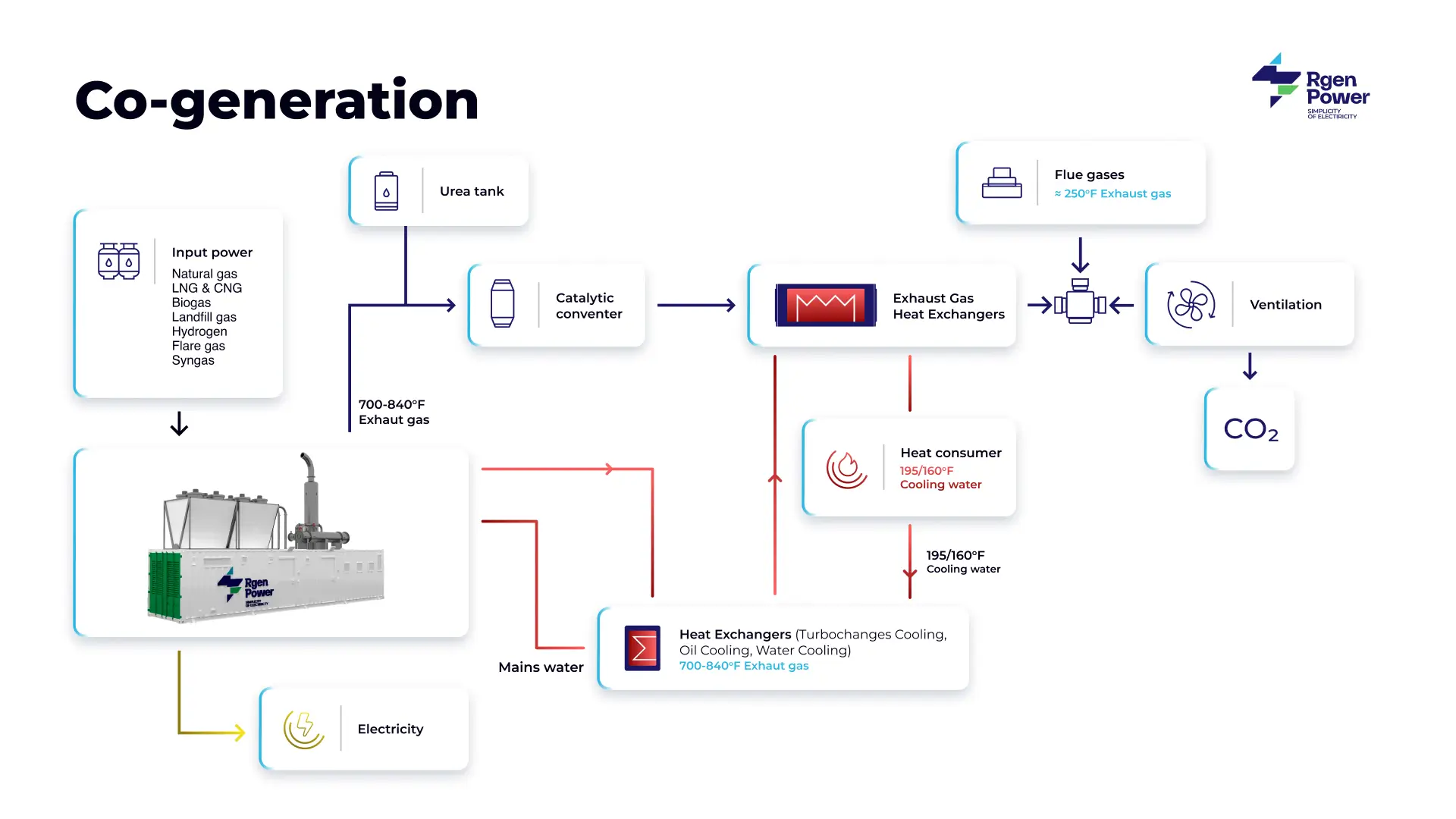
Combined Heat & Power Co-Generation (CHP) is a process of joint generation of electrical and thermal energy. Our company implements projects based on reciprocating engines that operate efficiently in cogeneration mode.








 Suite 515, 701 Brazos St, Austin, TX 78701
Suite 515, 701 Brazos St, Austin, TX 78701
 info@rgen-power.com
info@rgen-power.com
 +1-302-48-71-620
+1-302-48-71-620